Photo by Chris Liverani on Unsplash
Get Started with FastAPI: The Efficient Python Framework for Web Development
Part 2 of FastAPI development series
Table of contents
Now that we've covered some of the key features and benefits of FastAPI in our previous blog, let's dive into how to get started with the framework.
How to Get Started With FastAPI
- Installation: FastAPI can be installed using pip, the Python package manager. Simply run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install fastapi
pip install "uvicorn[standard]"
- Create a new project: To create a new FastAPI project, you can use any text editor or integrated development environment (IDE) of your choice. Create a new file named
main.pyand add the following code to get started:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
- Run the server: To run the FastAPI server, simply run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
uvicorn main:app --reload
This will start the FastAPI server, and you can access your API by visiting http://localhost:8000 in your web browser.
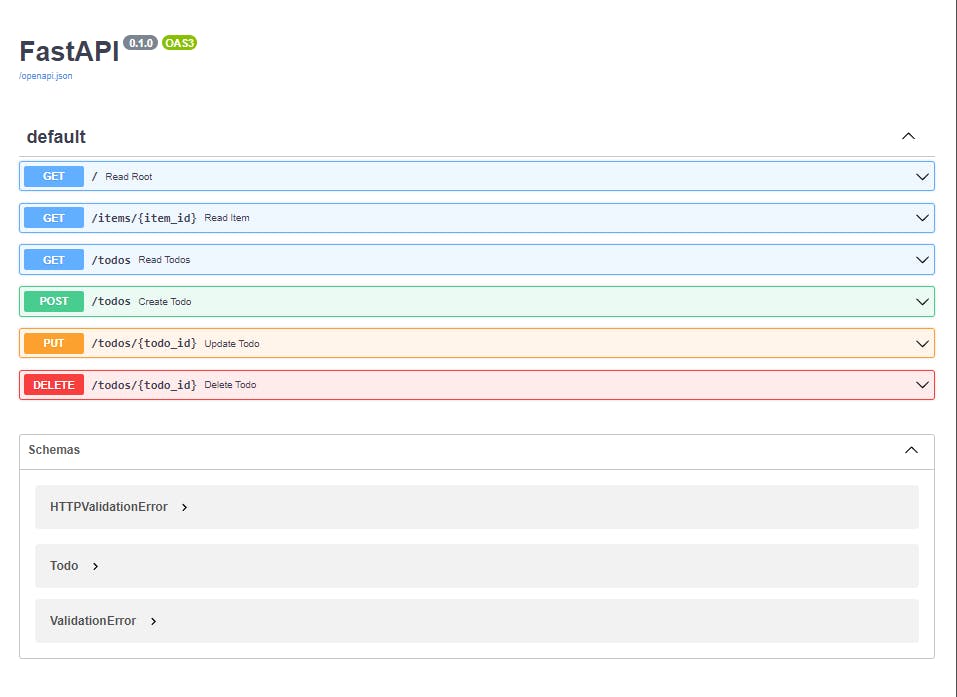
FastAPI Interactive API Documentation
One of the great things about FastAPI is its built-in, interactive API documentation. This allows you to easily see how your API is structured and test it out, without having to write any additional code.
To access the API documentation, visit http://localhost:8000/docs your web browser when the FastAPI server is running. The documentation provides a clear and intuitive interface for testing your API and exploring its functionality.
Building Your First Project with FastAPI
Now that you understand how to get started with FastAPI, let's build an easy project to get a feel for how it works.
For this project, we'll build a simple to-do list API. The API will allow you to add, read, update, and delete to-do items.
- Define the to-do model: First, let's define the to-do model by adding the following code to your
main.pyfile:
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Todo(BaseModel):
task: str
is_completed: bool = False
- Define the to-do list: Next, let's create a simple in-memory to-do list by adding the following code to your
main.pyfile:
todos = []
- Define the endpoints: Now, let's add the endpoint functions for adding, reading, updating, and deleting to-do items. Add the following code to your
main.pyfile:
@app.post("/todos")
async def create_todo(todo: Todo):
todos.append(todo)
return {"message": "Todo created successfully"}
@app.get("/todos")
async def read_todos():
return {"todos": todos}
@app.put("/todos/{todo_id}")
async def update_todo(todo_id: int, todo: Todo):
todos[todo_id] = todo
return {"message": "Todo updated successfully"}
@app.delete("/todos/{todo_id}")
async def delete_todo(todo_id: int):
todos.pop(todo_id)
return {"message": "Todo deleted successfully"}
- Test the endpoints: With the endpoints defined, you can now test the functionality of your to-do list API. You can use a tool like Postman or cURL to make requests to the API and verify that it's working as expected.
That's it! You've now built a simple to-do list API using FastAPI. This project is just a starting point, and there's plenty of room for further exploration and improvement.
In conclusion, FastAPI is a modern and efficient Python framework for building high-performance web applications and APIs. With its built-in features, including interactive API documentation and automatic data validation, FastAPI makes it easy to build and maintain your projects. Give it a try and see how it can help improve the performance of your next project.
Demo Gif


